Exchange Hybrid
The main goal of an Exchange hybrid deployment is that the customer enables the Exchange on-premises organization to move his on-premises mailboxes and public folders to Exchange Online.
But when the customer plan to start the Office 365 workloads and Exchange is not the first project, then you have to think about the dependencies of Exchange hybrid for example with Microsoft Teams.
This article describes the requirements for Exchange hybrid deployment not for Microsoft Teams.
Exchange hybrid deployment features
When you establish an Exchange hybrid deployment, you will get these additional features in your Exchange organization:
- Secure mail flow between on-premises and Exchange Online mailboxes
- Mail routing with the same accepted domains
- A global address list for on-premises and Exchange Online mailboxes
- Centralized inbound and outbound mail flow
- Sharing of Free/Busy information between on-premises and online users
- Move mailboxes from on-premises to Exchange Online and back to on-premises
Sources:
- Exchange Server hybrid deployments
- Learn more about Exchange Online Archiving at Archive Features in Exchange Online Archiving.
Requirements
To successfully establish an Exchange hybrid deployment your on-premises Exchange organization must meet the requirements.
- Exchange organizations from Version 2007 and later are supported
- Exchange organizations require the latest cumulative updates or update rollups. If this is not possible, install the previous one
- Exchange 2010 & Exchange 2013
- At least one server with the mailbox, hub transport, and client access server role must be installed
- If public folders are in use, install the client access server role on each mailbox server. This is needed to publish the public folder to Exchange Online users trough a public folder proxy mailbox on each mailbox server.
- Exchange Server 2016 and newer
- At least one server with mailbox server role installed
- Customer domains: Register any accepted domain from your on-premises Exchange organization in Office 365
- AzureAD Connect: You need an Active Directory synchronization between your on-premises Active Directory and your AzureAD tenant, read here for best practices: Secure Install of Azure AD Connect
- DNS Records: All these records must be published for any registered domain in your tenant
- Autodiscover
- Exchange Web Services
- Outlook on the Web
- Exchange organization publishing:
- Internal and external URLs must be configured correctly
- Internal and external access to the services must be configured and an external client must have access to the mailbox via Outlook on the Web and Outlook Anywhere
- Autodiscover must be published and accessible from external clients
- Publishing certificates: The certificates must be public, certificates from internal certification authorities are not supported.
- If you have different namespaces for IIS and SMTP, then you need for all services public certificates!
- Microsoft .Net Framework 4.6.2 or later is required to run the hybrid wizard
- If you have Unified Messaging enabled, see this article: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/hybrid-deployment-prerequisites
- Exchange Edge Server: If you plan to use Edge Server, remember that you have to configure some Exchange connectors manually
In my Exchange projects, I keep noticing that the company firewalls bring the project on halt. Take care that the firewalls meet the requirements for Exchange hybrid deployments.
See: Office 365 IPs and services
Check Remote Connectivity
To Test the external configuration and connectivity to your on-premises environment, you can use the Microsoft Remote connectivity analyzer to verify the needed connection.
Start http://aka.ms/exrca and test every domain that your users have as an reply address. Please test for each domain the following:
Exchange Server tests:
- Exchange Webservices
- Synchronization, Notification, Availability, and Automatic Replies
- Outlook
- Connectivity
- Autodiscover
Test Accepted Domain
For the tests above I created a PowerShell script, that does the job for you, but first, you need the list of accepted domains from your environment. please open your Exchange Server Powershell and type the following command and copy the output to your clipboard.
# Get a list of Accepted Domains
Get-AcceptedDomain | % { $Domains += ('"{0}",' -f $_.DomainName) }; $Domains.SubString(0,($Domains.Length -1))This script, you can download it from my GitHub account here, is needed to get a list of your domains with external access. After you download the script unblock the file with the following command.
Unblock-File -Path <PathToFile>Now you can run the Script with the -Domains parameter. The parameter accepts a comma-separated list of your domains, that list you get from the previous command “Get-AcceptedDomains”.
The script will check the following hosts for each domain:
- autodiscover
- outlook
- owa
- webmail
If the hostnames do not match your configuration of your Exchange Client Access URLs you can add the parameter -Hostnames to the script.
For example:
# Default run
.\Verify-ExternalAccessAndDNS.ps1 -Domains contoso.exlabs.de, fabrikarm.exlabs.de
# Run with other Hostnames
.\Verify-ExternalAccessAndDNS.ps1 -Domains contoso.exlabs.de, fabrikarm.exlabs.de -HostNames Webmail, OutlookThe output will show an output like this:
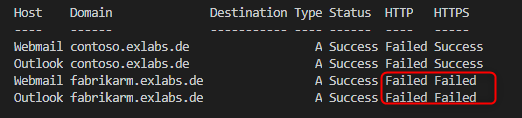
If you see that connections failed, you know you have something to do. 🙂
Access to Autodiscover must be available through HTTP and access to the Exchange Web Services, Outlook Anywhere and Outlook on the Web should be available through HTTPS.
Accepted Domains
Note: All accepted Domains in your on-premises Exchange organization should be activated as Exchange Online accepted domains! If you send an email from Exchange Online mailboxes to on-premises mailboxes, that have a primary address that is not registered as EXO accepted domain, the mail flow will not be marked as internal.
Additional information:
- Hybrid deployment prerequisites
- Add your domain to Office 365
- Learn more at Azure AD Connect User Sign-on options.
- Learn more at Hybrid management in Exchange hybrid deployments
- Learn more at Certificate requirements for hybrid deployments.
- Learn more at Edge Transport servers with hybrid deployments
- Office 365 IPs and services
- Learn more at Microsoft Remote Connectivity Analyzer.
- Learn more at Single sign-on with hybrid deployments.